Bladder Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
Bladder Cancer: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
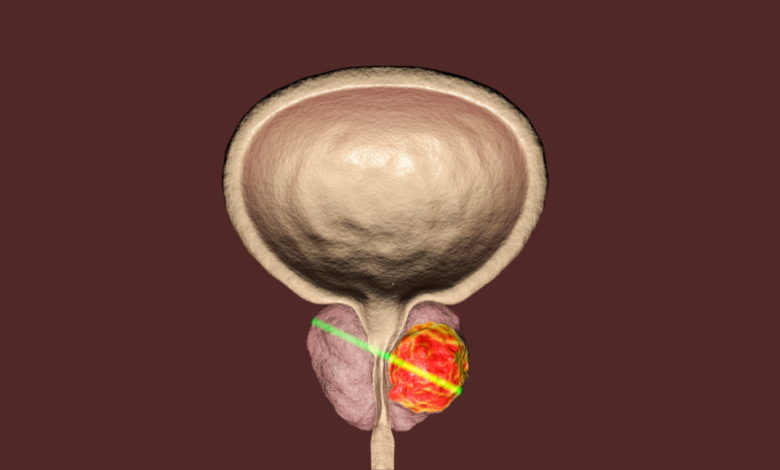
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the cells of the bladder, a hollow organ that stores urine.
Types of Bladder Cancer
The most common type of bladder cancer is urothelial carcinoma, which develops in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
Symptoms of bladder cancer can vary, but may include:
• Blood in the urine (hematuria)
• Frequent or urgent need to urinate
• Painful urination
• Difficulty urinating
• Lower back pain
Causes of Bladder Cancer
The exact causes of bladder cancer are not fully understood, but certain factors can increase the risk, including:
• Smoking: Smoking is the leading risk factor for bladder cancer.
• Exposure to certain chemicals: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those used in certain industries, can increase the risk.
• Older age: The risk of bladder cancer increases with age.
• Family history: A family history of bladder cancer can increase the risk.
Who Can Suffer from Bladder Cancer?
Anyone can develop bladder cancer, but it is more common in older adults and those who smoke.
Diagnostic Tests for Bladder Cancer
To diagnose bladder cancer, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Urinalysis: A urine test to check for blood or other abnormalities.
• Cystoscopy: A procedure to examine the bladder and urethra using a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed from the bladder lining and examined under a microscope.
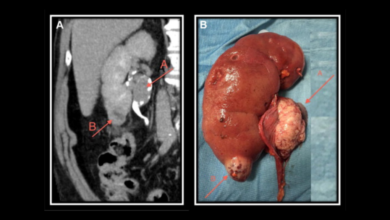
Stages of Bladder Cancer
The staging of bladder cancer helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
Treatment of Bladder Cancer
The treatment for bladder cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: Surgery may be used to remove the tumor or part of the bladder.
• Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells.
• Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
• Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system fight cancer cells.
Diet and Bladder Cancer Prevention
While a healthy diet can’t prevent bladder cancer, it can help maintain overall health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended.
Additionally, limiting exposure to certain chemicals and quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of bladder cancer.
Diet and Bladder Cancer Prevention
While a specific diet cannot guarantee prevention of bladder cancer, a healthy diet can contribute to overall health and may reduce the risk of certain cancers. Here are some dietary recommendations:
• Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and reduce the risk of urinary tract infections.
• Fruits and Vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, especially those high in antioxidants, can help protect cells from damage.
• Limit Processed Meats: Reducing consumption of processed meats, such as bacon, sausage, and hot dogs, may lower the risk of certain cancers.
• Moderate Caffeine Intake: Excessive caffeine intake might irritate the bladder.
• Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats from sources like fish, nuts, and olive oil.
Overall Survival Rate of Bladder Cancer
The overall survival rate for bladder cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, overall health, and the effectiveness of treatment. Early detection and timely treatment significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
A urologist is the best doctor to consult for bladder cancer.
Diseases Associated with Cancer
Bladder cancer is often associated with other health conditions, including:
• Smoking-related cancers: Lung, throat, and other cancers linked to smoking.
• Chronic urinary tract infections
• Exposure to certain chemicals: Occupational exposure to certain chemicals, such as aromatic amines, can increase the risk.
How to Prevent Bladder Cancer
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent bladder cancer, the following strategies can reduce the risk:
• Quit Smoking: Smoking is the leading risk factor for bladder cancer.
• Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins.
• Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
• Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect any abnormalities early on.
• Limit Exposure to Certain Chemicals: If you work in an industry that involves exposure to harmful chemicals, take necessary precautions.