Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Common Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Guide to Prevention and Detection

What is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
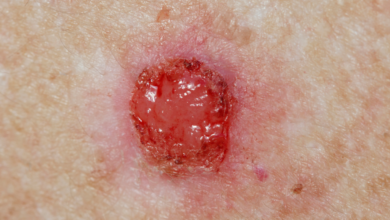
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It typically develops on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, neck, ears, and scalp.
Types of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinoma, including:
• Nodular basal cell carcinoma: The most common type, appearing as a pearly or waxy bump.
• Superficial basal cell carcinoma: A flat, scaly, or red patch on the skin.
• Infiltrating basal cell carcinoma: A more aggressive type that can grow deeper into the skin.
• Morpheaform basal cell carcinoma: A slow-growing, scar-like lesion.
Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Early-stage basal cell carcinoma may not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
• A pearly or waxy bump
• A red, scaly patch
• An open sore that bleeds or crusts
• A scar-like lesion
Causes of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The primary cause of basal cell carcinoma is excessive sun exposure. Other risk factors include:
• Fair skin: People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer.
• Family history of skin cancer: A family history of skin cancer can increase the risk.
• Weakened immune system: A weakened immune system can make it harder for the body to fight off skin cancer.
Who Can Suffer from Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Anyone can develop basal cell carcinoma, but people with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are at higher risk.
Diagnostic Tests for Basal Cell Carcinoma
To diagnose basal cell carcinoma, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Physical exam: A visual examination of the skin to check for any suspicious moles or growths.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Stages of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is typically not staged in the same way as other types of cancer. Instead, it is often classified based on its size and depth of invasion.
Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The treatment for basal cell carcinoma depends on the size, location, and type of the cancer. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the cancerous tumor and surrounding tissue.
• Mohs surgery: A specialized surgical technique to remove the cancer layer by layer.
• Cryotherapy: To freeze and destroy the cancer cells.
• Laser therapy: To destroy the cancer cells with a laser.
• Topical medications: To treat certain types of basal cell carcinoma.
Diet and Basal Cell Carcinoma Prevention
While a healthy diet can contribute to overall health, it cannot directly prevent basal cell carcinoma. However, limiting sun exposure and using sunscreen are the most effective ways to prevent this type of skin cancer.
Diet and Basal Cell Carcinoma Prevention
While a healthy diet can contribute to overall health, it cannot directly prevent basal cell carcinoma. However, maintaining a balanced diet can support the immune system and overall skin health.
Overall Survival Rate of Basal Cell Carcinomas
The overall survival rate for basal cell carcinoma is generally very high, especially if detected and treated early. With timely treatment, most cases of basal cell carcinoma can be cured.
Doctor to Consult
A dermatologist is the best doctor to consult for basal cell carcinoma.
Diseases Associated with Basal Cell Carcinomas
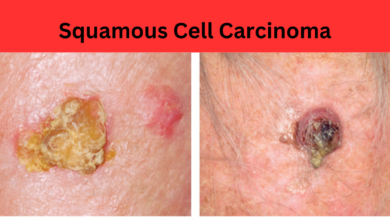
Basal cell carcinoma is primarily a skin cancer and is not directly linked to other specific diseases. However, it’s often associated with excessive sun exposure, which can also contribute to other skin problems and cancers, such as squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma.
How to Prevent Basal Cell Carcinomas
The most effective way to prevent basal cell carcinoma is to limit sun exposure and protect your skin from harmful UV radiation. Here are some tips:
• Limit sun exposure: Minimize time spent in direct sunlight, especially during peak hours.
• Use sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin.
• Wear protective clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing to protect your skin from the sun.
• Avoid tanning beds: Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation.
• Regular skin self-exams: Check your skin regularly for any changes, such as new moles or changes in existing moles.
• Regular skin exams: Schedule regular skin exams with a dermatologist.