Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rare but Aggressive Skin Cancer
Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Understanding a Rare Skin Cancer
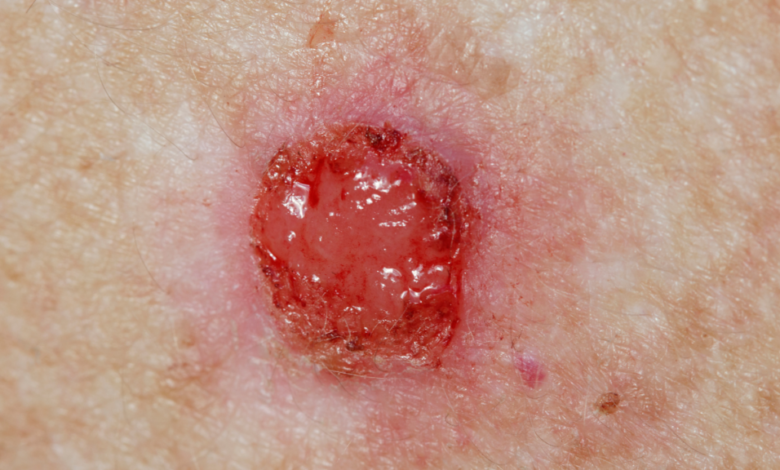
What is Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
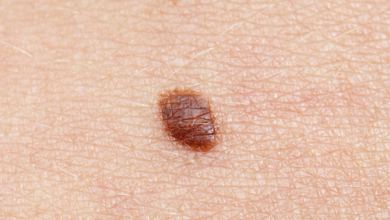
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare but aggressive type of skin cancer that develops in Merkel cells, which are specialized cells found in the lowest layer of the epidermis.
Types of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
While there aren’t distinct subtypes of Merkel cell carcinoma, it can be classified based on its stage and the presence of certain genetic mutations.
Symptoms of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma often appears as a:
• Red, painless, or slightly itchy lump
• Firm, shiny nodule
• Purple or reddish-blue bump
Causes of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The exact cause of Merkel cell carcinoma is not fully understood. However, certain factors can increase the risk, including:
• Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation: Excessive sun exposure is a major risk factor.
• Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at increased risk.
• Exposure to certain viruses: Infection with Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) is associated with the development of Merkel cell carcinoma.
Who Can Suffer from Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
Anyone can develop Merkel cell carcinoma, but it is more common in older adults and people with weakened immune systems.
Diagnostic Tests for Merkel Cell Carcinoma
To diagnose Merkel cell carcinoma, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
• Imaging tests: CT scans and MRIs can help determine the extent of the cancer.
Stages of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The staging of Merkel cell carcinoma helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
Treatment of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The treatment for Merkel cell carcinoma depends on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the cancerous tumor and surrounding tissue.
• Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells with high-energy rays.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Immunotherapy: To boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
Diet and Merkel Cell Carcinoma Prevention
While a healthy diet can contribute to overall health, it cannot directly prevent Merkel cell carcinoma. However, limiting sun exposure and using sunscreen can significantly reduce the risk.
Diet and Merkel Cell Carcinoma Prevention
While a healthy diet can contribute to overall health, it cannot directly prevent Merkel cell carcinoma. The primary preventive measure is limiting sun exposure.
Overall Survival Rate of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
The overall survival rate for Merkel cell carcinoma varies depending on the stage of the cancer, the type of treatment received, and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and aggressive treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
A dermatologist or a medical oncologist is the best doctor to consult for Merkel cell carcinoma.
Diseases Associated with Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is primarily associated with exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Additionally, it’s linked to infection with Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV).
How to Prevent Merkel Cell Carcinoma
To prevent Merkel cell carcinoma, consider the following:
• Limit sun exposure: Minimize sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
• Use sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
• Wear protective clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and long-sleeved clothing to protect your skin from the sun.
• Avoid tanning beds: Tanning beds emit harmful UV radiation.
• Regular skin self-exams: Check your skin regularly for any changes, such as new moles or changes in existing moles.
• Regular skin exams: Schedule regular skin exams with a dermatologist.