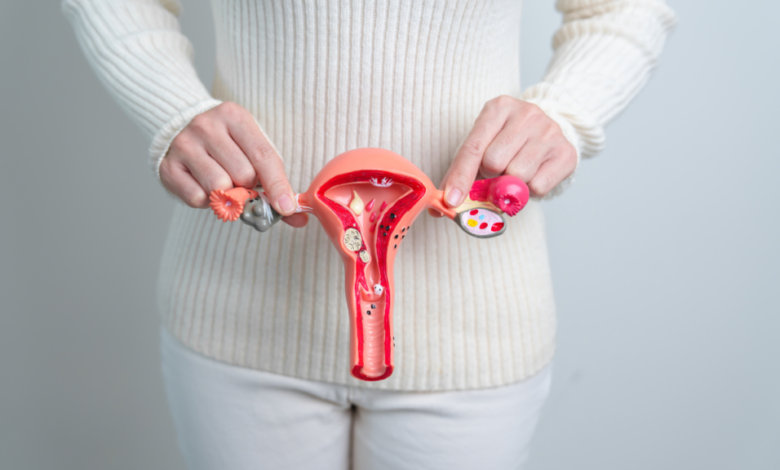
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the ovaries, the female reproductive organs that produce eggs.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
There are several types of ovarian cancer, but the most common is epithelial ovarian cancer. Other less common types include germ cell tumors and stromal tumors.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Early-stage ovarian cancer often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
• Bloating
• Pelvic or abdominal pain
• Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
• Frequent urination or urgency
• Changes in bowel habits
• Fatigue
• Back pain
• Weight loss
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown. However, certain factors can increase the risk, including:
• Family history: A family history of ovarian cancer or certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk.
• Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after menopause.
• Hormone therapy: Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy can slightly increase the risk.
Who Can Suffer from Ovarian Cancer?
Women can develop ovarian cancer. However, the risk is higher in older women and those with a family history of the disease.
Diagnostic Tests for Ovarian Cancer
Early detection of ovarian cancer can be challenging. Tests may include:
• Pelvic exam: A physical exam of the pelvic area.
• Pelvic ultrasound: An ultrasound to visualize the ovaries and uterus.
• CA-125 blood test: A blood test to measure the level of a protein called CA-125, which can be elevated in some ovarian cancers.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed from the ovary and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Stages of Ovarian Cancer
The staging of ovarian cancer helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the FIGO staging system, which considers the size of the tumor, the spread to nearby tissues and organs, and the presence of distant metastases.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
The treatment for ovarian cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Targeted therapy: To target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
Diet and Ovarian Cancer Prevention
While a healthy diet can’t guarantee prevention of ovarian cancer, a balanced diet can contribute to overall health and may reduce the risk of certain cancers. Here are some dietary recommendations:
• A balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
• Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: These can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for ovarian cancer.
Diet to Prevent Ovarian Cancer
While there’s no specific diet that can guarantee prevention of ovarian cancer, a healthy diet can contribute to overall health and may reduce the risk of certain cancers. Here are some dietary recommendations:
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for ovarian cancer.
• Limit red meat and processed meat: Consuming too much red and processed meat can increase the risk of certain cancers.
• Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help.
• Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of certain cancers.
Overall Survival Rate of Ovarian Cancer
The overall survival rate for ovarian cancer varies depending on the stage of the cancer, the type of treatment received, and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and timely treatment significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
A gynecologist or a gynecologic oncologist is the best doctor to consult for ovarian cancer.
Diseases Associated with Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is often associated with certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, which can increase the risk of ovarian cancer and other cancers.
How to Prevent Ovarian Cancer
In addition to a healthy diet, the following strategies can help prevent ovarian cancer:
• Regular gynecological check-ups: Regular pelvic exams and Pap smears can help detect early signs of cancer.
• Family history screening: If you have a family history of ovarian cancer, consider genetic testing to assess your risk.
• Hormone therapy: Use hormone replacement therapy for the shortest duration possible and under the supervision of a healthcare provider.