Penile Cancer: A Rare Type of Cancer
Penile Cancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment

What is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer is a rare type of cancer that develops in the cells of the penis.
Types of Penile Cancer
The most common type of penile cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which develops in the squamous cells that line the penis.
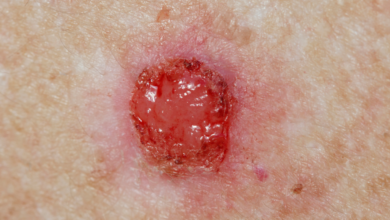
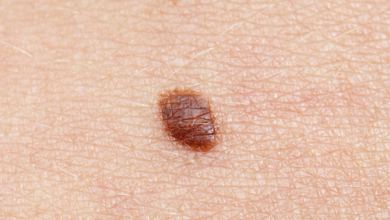
Symptoms of Penile Cancer
Early-stage penile cancer often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
• A sore on the penis that doesn’t heal
• A lump or thickening on the penis
• Changes in the color of the penis
• Unusual discharge from the penis
• Pain or discomfort in the penis
Causes of Penile Cancer
The exact causes of penile cancer are not fully understood, but certain factors can increase the risk, including:
• Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Certain types of HPV can increase the risk of penile cancer.
• Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of penile cancer.
• Poor hygiene: Poor hygiene can increase the risk of infection, which may contribute to cancer development.
• Phimosis: A condition in which the foreskin cannot be retracted over the head of the penis.
Who Can Suffer from Penile Cancer?
Men can develop penile cancer. However, it is relatively rare.
Diagnostic Tests for Penile Cancer
To diagnose penile cancer, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Physical exam: A physical examination of the penis and genitals.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed from the penis and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
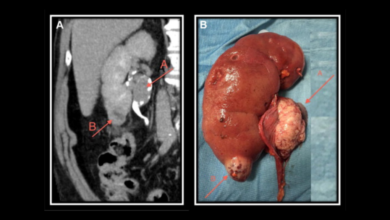
• Imaging tests: CT scans and MRIs may be used to determine the extent of the cancer.
Stages of Penile Cancer
The staging of penile cancer helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
Treatment of Penile Cancer
The treatment for penile cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the cancerous tumor and, in some cases, part of the penis.
• Mohs surgery: A specialized surgical technique to remove the cancer layer by layer.
• Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells with high-energy rays.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
Diet and Penile Cancer Prevention
While a healthy diet can contribute to overall health, it cannot directly prevent penile cancer. However, a balanced diet can support the immune system, which plays a role in fighting off infections, including HPV, a risk factor for penile cancer.
Here are some general dietary tips for overall health:
• A balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help.
• Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: These can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can increase the risk of certain health problems.
Overall Survival Rate of Penile Cancer
The overall survival rate for penile cancer varies depending on the stage of the cancer, the type of treatment received, and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and timely treatment significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
A urologist is the best doctor to consult for penile cancer.
Diseases Associated with Penile Cancer
Penile cancer is primarily associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can increase the risk of various cancers, including penile cancer, anal cancer, and oropharyngeal cancer.
How to Prevent Penile Cancer
To prevent penile cancer, consider the following:
• HPV vaccination: Getting vaccinated against HPV can significantly reduce the risk of penile cancer.
• Safe sex practices: Using condoms can help prevent HPV infection.
• Good hygiene: Maintaining good hygiene can help prevent infections.
• Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect any abnormalities early on.