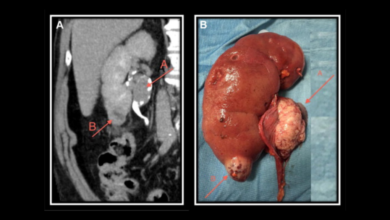
What is Kidney Cancer?
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma, is a type of cancer that develops in the kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, below the ribs and behind the abdominal cavity.
Types of Kidney Cancer
The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma. Other less common types include:
• Transitional cell carcinoma: This type of cancer affects the lining of the renal pelvis and ureters.
• Collecting duct carcinoma: A rare type of cancer that develops in the collecting ducts of the kidney.
Symptoms of Kidney Cancer
Early-stage kidney cancer often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
• Blood in the urine
• Pain in the side or back
• A lump in the side or back
• Fatigue
• Weight loss
• Fever
• Loss of appetite
Causes of Kidney Cancer
The exact causes of kidney cancer are not fully understood. However, certain factors can increase the risk, including:
• Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for kidney cancer.
• Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk.
• High blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of cancer.
• Family history: A family history of kidney cancer can increase the risk.
• Certain genetic conditions: Certain genetic conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau disease, can increase the risk.
Who Can Suffer from Kidney Cancer?
Anyone can develop kidney cancer, but it is more common in older adults. Men are more likely to develop kidney cancer than women.
Diagnostic Tests for Kidney Cancer
To diagnose kidney cancer, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Blood tests: To check kidney function and for other abnormalities.
• Urine tests: To check for blood or other abnormalities in the urine.
• Imaging tests: CT scans and ultrasounds can help visualize the kidneys and detect any abnormalities.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Stages of Kidney Cancer
The staging of kidney cancer helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
Treatment of Kidney Cancer
The treatment for kidney cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the kidney or part of the kidney containing the tumor.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Immunotherapy: To boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
• Targeted therapy: To target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
Diet and Kidney Cancer Prevention
While a specific diet cannot guarantee prevention of kidney cancer, a healthy diet can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk. Here are some dietary recommendations:
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for kidney cancer.
• Limit red meat: Excessive consumption of red meat has been linked to an increased risk of kidney cancer.
• Increase intake of fruits and vegetables: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can provide essential nutrients and antioxidants.
• Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and maintain kidney health.
• Limit sodium intake: High sodium intake can increase blood pressure, which is a risk factor for kidney disease.
Overall Survival Rate of Kidney Cancer
The overall survival rate for kidney cancer varies depending on the stage of the cancer, the type of treatment received, and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and timely treatment significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
A urologist is the best doctor to consult for kidney cancer.
Diseases Associated with Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer can be associated with certain genetic conditions, such as:
• Von Hippel-Lindau disease: This genetic disorder increases the risk of developing various types of cancer, including kidney cancer.
• Hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma: This inherited condition increases the risk of kidney cancer.
How to Prevent Kidney Cancer
In addition to a healthy diet, the following strategies can help prevent kidney cancer:
• Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for kidney cancer.
• Control blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage the kidneys.
• Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect any abnormalities early on.