Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
What is Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)?
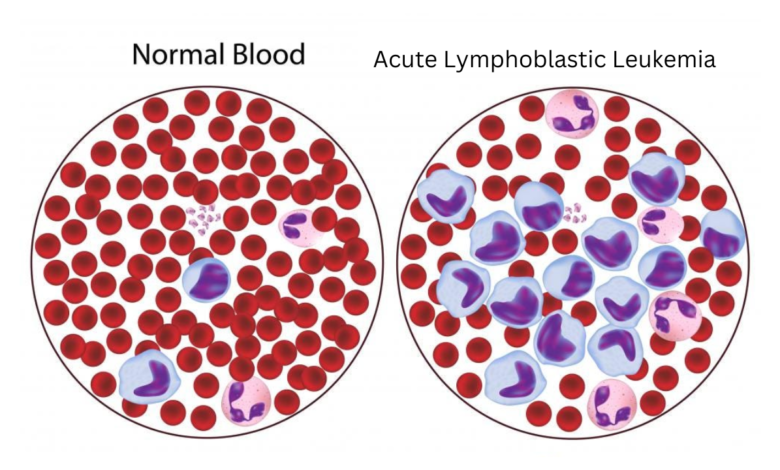
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells. In ALL, the bone marrow produces too many immature white blood cells, called lymphoblasts. These abnormal cells crowd out healthy blood cells, leading to various health problems.
Types of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL is primarily categorized based on the type of white blood cell affected and the genetic abnormalities present in the cancer cells. However, the specific subtypes are complex and often require specialized testing for accurate classification.
Symptoms of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Symptoms of ALL can vary but often include:
• Fatigue
• Frequent infections
• Easy bleeding or bruising
• Fever
• Night sweats
• Weight loss
• Bone pain
• Swollen lymph nodes
• Enlarged liver or spleen
Causes of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
The exact cause of ALL is often unknown. However, certain factors may increase the risk, including:
• Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk.
• Exposure to radiation or certain chemicals: Exposure to these substances can increase the risk.
• Immune system disorders: Some immune system disorders can increase the risk.
Who Can Suffer from Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)?
ALL primarily affects children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
Diagnostic Tests for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
To diagnose ALL, a doctor may use a combination of tests, including:
• Complete blood count (CBC): To check for abnormalities in the blood cells.
• Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: To examine bone marrow cells.
• Lumbar puncture: To check for cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
• Flow cytometry: A laboratory technique to identify specific types of cells.
• Genetic testing: To identify specific genetic abnormalities associated with ALL.
Stages of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL is not typically staged in the same way as solid tumors. Instead, it is classified based on the risk factors and the patient’s response to treatment.
Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
The treatment for ALL typically involves a combination of therapies, including:
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells in specific areas.
• Stem cell transplantation: To replace damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
Diet and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Prevention
While a healthy diet can support overall health, it cannot directly prevent ALL. However, a balanced diet can help maintain a strong immune system, which is crucial for fighting infections and cancer.
Here are some general dietary tips:
• A balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
• Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: These can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.
Diet and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Prevention
While a healthy diet can support overall health and strengthen the immune system, it cannot directly prevent ALL. However, a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being and help the body fight infections.
Overall Survival Rate of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
The overall survival rate for ALL has significantly improved over the years, especially for children. However, the prognosis varies depending on factors like the patient’s age, the specific type of ALL, and the response to treatment. Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are crucial for a better outcome.
Doctor to Consult
A hematologist-oncologist is the best doctor to consult for ALL.
Diseases Associated with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL is not directly associated with other specific diseases. However, certain genetic factors and environmental exposures can increase the risk of developing ALL.
How to Prevent Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent ALL, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of certain factors that may contribute to the disease:
• Limit exposure to radiation and certain chemicals: Exposure to these substances can increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.
• Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups can help detect any abnormalities early on.
• Healthy lifestyle: A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help boost the immune system.