Adenocarcinomas: A Common Type of Cancer
Adenocarcinoma: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is Adenocarcinoma?
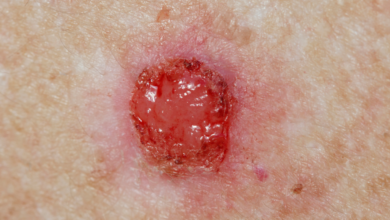
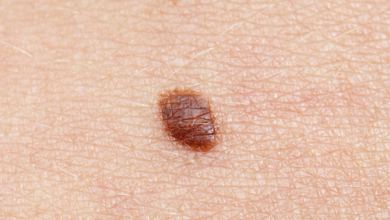
Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that originates in glandular cells, which are cells that produce and secrete substances. These glands are found in various organs throughout the body.
Types of Adenocarcinomas
Adenocarcinomas can develop in many different organs, including:
• Lung: Lung adenocarcinoma is a common type of lung cancer.
• Colon and Rectum: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of colon and rectal cancer.
• Stomach: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of stomach cancer.
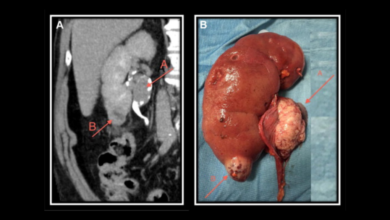
• Pancreas: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of pancreatic cancer.
• Breast: Invasive ductal carcinoma, a type of breast cancer, is an adenocarcinoma.
• Prostate: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of prostate cancer.
• Thyroid: Adenocarcinoma can develop in the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of Adenocarcinomas
The symptoms of adenocarcinoma can vary depending on the organ affected. However, some general symptoms may include:
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fatigue
• Fever
• Night sweats
• Pain
• Changes in bowel or bladder habits
Causes of Adenocarcinomas
The exact causes of adenocarcinoma can vary depending on the specific type and location. However, some common risk factors include:
• Smoking: A major risk factor for lung, pancreatic, and other cancers.
• Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can increase the risk of certain cancers.
• Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk of certain cancers.
• Family history: A family history of cancer can increase the risk.
• Certain infections: Infections with certain viruses, such as HPV and hepatitis B and C, can increase the risk of certain cancers.
Who Can Suffer from Adenocarcinomas?
Anyone can develop adenocarcinoma, but the risk factors and prevalence can vary depending on the specific type of adenocarcinoma.
Diagnostic Tests for Adenocarcinomas
The diagnostic tests for adenocarcinoma will vary depending on the location of the cancer. However, common tests may include:
• Imaging tests: CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds can help visualize the tumor and determine its extent.
• Biopsy: A small tissue sample is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
• Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for tumor markers or other abnormalities.
Stages of Adenocarcinomas
The staging of adenocarcinoma helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the size of the tumor (T), the spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
Treatment of Adenocarcinomas
The treatment for adenocarcinoma depends on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the cancerous tumor and surrounding tissue.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells with high-energy rays.
• Targeted therapy: To target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
Treatment of Adenocarcinomas
The treatment for adenocarcinoma depends on the specific type, location, and stage of the cancer. Common treatment options include:
• Surgery: To remove the cancerous tumor and surrounding tissue.
• Chemotherapy: To kill cancer cells throughout the body.
• Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells with high-energy rays.
• Targeted therapy: To target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
• Immunotherapy: To boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
Diet and Adenocarcinoma Prevention
While a specific diet cannot guarantee prevention of all types of adenocarcinoma, a healthy diet can reduce the risk of certain cancers. Here are some general dietary recommendations:
• A balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
• Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: These can contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of certain cancers.
• Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of certain cancers.
Overall Survival Rate of Adenocarcinomas
The overall survival rate for adenocarcinoma varies significantly depending on the specific type and location of the cancer, as well as the stage of the disease and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and timely treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
Doctor to Consult
The specific doctor who treats adenocarcinoma will depend on the location of the cancer. For example:
• Lung cancer: Pulmonologist or thoracic surgeon
• Colon and rectal cancer: Gastroenterologist or colorectal surgeon
• Stomach cancer: Gastroenterologist
• Pancreatic cancer: Gastroenterologist or surgical oncologist
• Breast cancer: Breast surgeon or medical oncologist
• Prostate cancer: Urologist
• Thyroid cancer: Endocrinologist or surgeon
Diseases Associated with Adenocarcinomas
Adenocarcinomas are often associated with other health conditions, such as:
• Chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation can increase the risk of certain types of adenocarcinoma, such as colon cancer and pancreatic cancer.
• Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of specific types of adenocarcinoma, such as hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome.
• Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as smoking and radiation, can increase the risk of lung cancer and other types of adenocarcinoma.
How to Prevent Adenocarcinomas
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent all types of adenocarcinoma, the following strategies can reduce the risk of certain cancers:
• Avoid smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for lung cancer and other cancers.
• Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of certain cancers.
• Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer.
• Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help.
• Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups can help detect cancer early.
• Get vaccinated: Vaccines for HPV and hepatitis B can help prevent certain types of cancer.